Staying focused in a day to day life

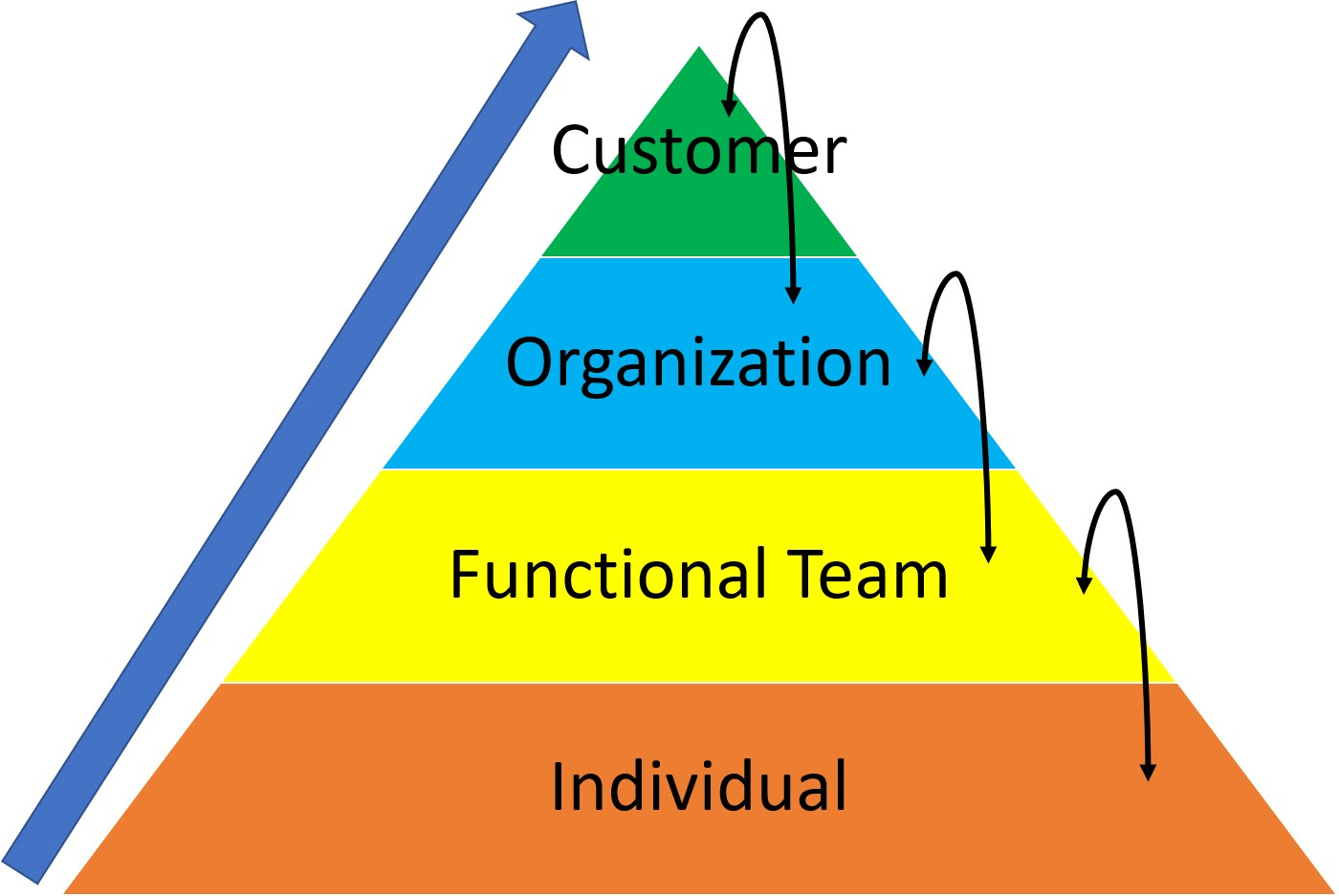
Now let us discuss how effectively people stay focused in day-to-day activities/micro level / individual level.
It is very challenging to remain focused on our daily activities and results as distractions may be created by ourselves through our practices and others. Some effective people overcome by consciously practicing some behaviors which i observe and learn from them.
- They have clarity about what they want or what agenda to fulfill in a day.
- They maintain a "To do list" on a piece of paper and ensure to check at the end of the day.
- They convert their agenda into key performance indicators (KPIs) that they measure and track periodically. We speak ideas most and forget them, but converting the idea into metrics will improve the focus.
- They will always start with END. This habit will help them focus on the result rather than being distracted by the activities.
- They are more prudent about "what not to do or what not to talk" about than what to do. Focus is all about what not to do and what to do.
- They manage and conduct the meetings very well, as distractions mostly happen in meeting forums. They organize themselves very well by certain behaviors like putting the mobile in silent mode, going by the agenda, taking notes, and involving all stakeholders.
- Even if someone distracts from the agenda, they will bring it back to the agenda quickly as they know it is one of the core jobs of chairing the meetings. Sometimes when the discussion gets into conflict, they brilliantly handle it or, worst case, make it offline to remain focused.
You might have observed the above behaviors and something more.
The point is that staying focused is a choice irrespective of the environment, and this is one of the mindsets that help us to stay focused. When we, as leaders/managers, remain focused, the team will also stay focused and enable us to get things done.
Have a great week ahead.