- One of the primary responsibilities of a manager/ leader is to make decisions on any workplace challenges at the right time, given the facts and assumptions. Whether the decision is right or wrong, time will decide. It is better to make decisions rather than be indecisive.
- When we make a series of decisions that yield results, it eventually improves our self-confidence.
- As emotions overdrive logic, we need to be aware of emotions vs. reasoning in decision-making situations.
- Everyone will go through a decision dilemma, and one of the approaches to overcome it is to go through the " Decision Vs. Consequence" matrix, as it will give clarity to move forward.
- Understanding the problem and defining it RIGHTLY will be the first step in problem-solving
- As a manager/leader, which problem do we solve most of the time, " Adhoc or Chronic"? The answer will tell our managerial time spending and effectiveness.
- All chronic problem needs structured problem-solving methodologies, and everyone should learn the process of the structured problem-solving process.
- Prioritizing the problem itself is an art as there are numerous problems one has to solve. One approach we discussed was using the " Complexity Vs. Impact" matrix.
- Developing the "Data Skill" is a must for professional development. This skill includes the ability to collect the suitable data set, analyze and remove noises, see some patterns, converge on root causes, and sell the ideas to others and implementation.
- Most technical and managerial problems result from a lack of people and processes. Please be sure to look for the root causes from this perspective as it helps you to reach the solutions quickly.
- Selling ideas to others is essential apart from data analysis. We discussed some of the hurdles like self-doubt, fear of rejection, and fear of failure. We also discussed the solution approach to overcome the limitations.
- Developing Action Plan is a managerial art; developing the skill will improve communication.
- We discussed the checklist for decision-making, and one profound list is putting the highest stakeholders as a focal point to make the right decision.
- We also discussed the leadership patterns in creating a conducive decision-making environment in the organization where people love to work for the manager/leader.
- Ultimately, a senior professional is paid for deciding at the right time for the challenges. It calls for probelm solving and decision-making skill development. It can be acquired by awareness and practice.
Perspective sharing and learning to improve personal and professional growth.....
Tuesday, 18 October 2022
Summarising- Developing decision making skill
Saturday, 3 September 2022
Leadership patterns for a positive decision-making environment (contd..)

Some of the patterns listed as i observed from many outstanding managers/leaders.
- Clarity on the problem & delegation level
- Communication & expectation setting on solving the problem
- Switching between micro & macro management of detailing
- Space for risk-taking & learning attitude to deal with failure
Having discussed the three patterns, let us understand how leaders create space for risk-taking and failure.
Space for risk-taking & learning attitude to deal with failure :
Some managers and leaders, as i observed, insist people take new initiatives apart from routine activities even though any new initiatives have the probability of 50 % success.
My first manager in my career always engaged himself in new initiatives, and half of it turned into failure only. Despite he did experiments and also encouraged others to do something new. More than that, when the initiatives failed and cost the organization, he always defended the team's intent and effort than the results. Hence, he was among the outstanding managers regarded by peers, and people loved working with him.
Also, some leaders encourage the team to learn from the failure and perceive it as experience. My friend, an entrepreneur, always uses the phrase " it is part of learning" whenever his effort fails in any new initiatives, and he moves on to the next.
When the leader always insists on learning and encourages the people to experiment, the people would show interest in solving the problem and dare to make decisions without fear.
Nowadays, large-size organizations encourage innovation projects by rewarding people for daring to do new experiments. A classic example is the TATA Group's initiative promoting innovations through the "Tata Innovista " program. Through this program, teams are recognized and rewarded every year for success and failure in innovative projects. The Management believes in experimentation and risk-taking.
To sum up,
- It is the leaders/managers who create a conducive environment through their behavior, communication, and process for the people to take the lead on the problem-solving and decision-making enhancement.
- Creating such a conducive environment is what leadership is all about and expected from managers and leaders.
Have a great week ahead.
Leadership patterns for a positive decision-making environment (contd..)
Some of the patterns listed as i observed from many outstanding managers/leaders.
- Clarity on the problem & delegation level
- Communication & expectation setting on solving the problem
- Switching between micro & macro management of detailing
- Space for risk-taking & learning attitude to deal with risk and failure
Having discussed the first two patterns, let us understand the ability to switch in and out on the management of details.
Switching between micro & macro management :
Influential managers/ leaders are aware of the management process and can converge and diverge on the problem-solving process.

Some people take an extreme stand on macro management and leave the execution of tasks to others, assuming they empower others. Some people try to get into all the nitty-gritty of the job, thinking they help others get things done. Each stand affects the problem-solving and decision-making capabilities of people reporting to them.
Consider the case, as i observed,
One of the business heads is balancing the micro and macro level of management. His style of leadership makes his team get things done with little effort.
For example, when he wants to conduct an event, he calls his team, explains his end objective, and leaves it to the team on execution details (Macro management). He is disciplined enough to review the progress. When the team raises some concerns, say cross-functional conflict, he gets into detailing (micromanagement) and clears the path (macro). It looks like he is nowhere connected to the team, and at the same time, he is available for guidance when required. His style is a standard management process, but there is a subtle difference between being in and out of the task and empowering the people. It is an art.
Because of his switching between macro and micro-management styles, the team feels comfortable working with him and problem-solving, and decision-making capabilities are enhanced among the group, as i witnessed.
Balancing macro and micro-management calls for introspection of our thought process towards work and people. However, the ability can be learned.
Have a great week ahead.
Leadership patterns for a positive decision-making environment

Last week we discussed some of the leadership patterns effective managers/ leaders display to create a positive environment for problem-solving and decision-making in the organization.
Some of the patterns listed as i observed from many outstanding managers/leaders.
- Clarity on the problem & delegation level
- Communication & expectation setting on solving the problem
- Switching between micro & macro management of detailing
- Space for risk-taking & learning attitude to deal with risk and failure
Having discussed the "clarity and delegation level" last week, let us understand more about communication
Communication and expectation setting on solving problems:
Effective managers are good at setting their expectations from others on solving problems and decision-making through their communication process.
One of my colleagues always asks his team members "what can be done "and "what else can be done" when someone approaches him with a problem. He is good at his functional domain and intends to solve the problem; however, instead of giving brief instructions, he prompts others with his communication style and encourages people to think and generate alternative options for solving the problem.
No surprise that everyone regards him as one of the best managers as everyone is comfortable working with him, and most of the time, the problems are getting resolved quickly.
My observation of his communication style and the impact are as follows
- The team is aware of approaching him with options than merely elevating the problem
- When the team thinks and generates the options, they conclude the suitable options most of the time, and issues are not elevated to his level
- Since the team approaches him with multiple options and when he endorses some options, that behavior reinforces the team's confidence in solving the problem and decision-making capability
The effective manager creates a "positive and inclusive problem-solving and decision-making environment through this communication process."
Let us discuss other patterns of "Micro vs. Macro detailing" next week.
Have a great week ahead!
Leadership patterns in a decision-making environment
Leadership patterns in a decision-making environment
Managers/Leaders create an environment by their functioning and style, which determines the organization's decision-making capability.
Let me summarise some of the patterns i have observed in many outstanding managers/leaders.
- Clarity on the problem and delegation level
- Communication and expectation setting on solving the problem
- Switching between micro & macro management of detailing
- Space for risk-taking and learning attitude to deal with risk and failure
Clarity on the problem and delegation level :
Effective manager/ leader is good at developing clarity on what needs to be delegated and what must be solved by themselves. They create clarity based on the intensity of the problem and its impact, timeline pressure, and the team's competency level.

In a good case, in one of the organizations, a manager makes the decision every day on what needs to be produced and how much needs to be produced and just delegates the team to comply. He is not delegating the production planning. Since he is only aware of the big picture of change in customer preference, internal capacity, team's influence on each other, and the impact of the delayed decision on business deliverables, he makes decisions himself.No more complexity in the system on decision making.
Whereas in another case, one organization always runs with a crisis on the working capital issues, and the business head expects the production head and finance head to take decisions on priority. Since the impact of the decisions would affect the deliveries, the functional heads either delays the decision or are indecisive most of the time. The environment becomes chaotic as each one points out others for their problem-solving and decision-making speed and quality. The cause of the problem is over delegation of critical issues to inappropriate people and expecting fast decision-making and problem-solving.
In both cases, the underlying factor is getting clarity on which problem we need to delegate and setting the expectation on problem-solving and decision-making at the team's level.
When we do not have the clarity to distinguish, as a manager/leader we create an environment with unrealistic expectations.
Some effective managers/ leaders are good at differentiating the problem, the impact of the problem, and the level of delegation by which they set the right environment for timely decision-making and problem-solving.
Let us discuss other leadership patterns next week.
Tuesday, 30 August 2022
Managerial style Vs. Team's decision-making capability
One of the concerns most business heads/managers have is how to bring the problem-solving and decision-making capabilities among the team?
This genuine concern comes from the reality that they spend more time giving instructions/ decisions on many routine tasks as people approach them and also from the feeling that they could not devote time to significant problems or value addition where they can only do it.
The concern needs to approach from two aspects. One is on more profound education or awareness of the importance of problem-solving competency, methodologies, tools, and techniques. Learning to some extent helps the team to improve their problem-solving & decision-making abilities.
However, as a second aspect, to a large extent, it is the business head/manager’s managerial style that determines the organizational environment for the team to take the lead on problem-solving and decision-making in any situation.
Hence the first aspect can be more straightforward than the second aspect of relooking the manager’s style of getting things done.
For example, consider the type of managers/leaders we might have come across in the organization.
Category 1:
The type of managers/leaders who do not want to hear any problem or bad news and used to say to the team, “Don’t bring me the problem only, come with solutions.”
 Sometimes they spend time with the team to resolve the problem. They display both distant and friendly behavior towards problem-solving. Uncertainty in predicting the behavior.
Sometimes they spend time with the team to resolve the problem. They display both distant and friendly behavior towards problem-solving. Uncertainty in predicting the behavior.In this environment, the team is likely reluctant to take the lead in solving the problem independently and clueless about the expectation of problem-solving and decision-making.
Category 2:
The type of managers/ leaders who enjoy solving the problem themselves. Their pride
 is in solving an issue of any kind and operating with the belief that their core responsibility is to solve the problem irrespective of assigning ownership.
is in solving an issue of any kind and operating with the belief that their core responsibility is to solve the problem irrespective of assigning ownership. Likely, in this environment, the managers will resolve all the issues, and the team will be open enough to escalate the problem. They think problem-solving is all about escalation to the boss, and the scope for enhancing problem-solving and decision-making competency will be limited.
Category 3:
These managers/leaders believe in the larger goal, define the escalation process and ownership, good at delegating and empowering the team to make decisions. They pitch only when there is an escalation to their level and is also disciplined enough to make the people accountable for the task through clarity and periodic reviews.
Likely, in this environment, people are reasonably good at problem-solving and decision-making and enjoy learning more from the boss.
In all the categories, the managers/leaders have a good intention of getting things done, and no one will resemble the same type all the time; it will be a combination of all styles depending on the situation. However, what category or style one demonstrates most of the time determines the team’s problem-solving and decision-making capability.
If the managers/ leaders are aware of their style, delegation, communication process, and change in style lead to change in the organizational environment for enhancing decision-making capabilities among the team.
We can talk about some of the strategies for each type of category next week.
Until then, you relate to your managerial style in most of the time and how good your team’s capability in problem-solving and decision-making.
Have a great week ahead.
Friday, 12 August 2022
a simple guide for the right decision making
a simple guide for the right decision making
The question was, " how to balance the boss and the junior colleagues?".
He seems to find it challenging to manage his boss and junior colleagues as some of his decisions went against him. This situation is common as most middle-level managers go through in a day to day life in the organization.
My view is as follows.
We do not need to balance any stakeholders with our decisions other than how to make the right decision so that the impact would be more significant and we will not feel guilty about the consequence.
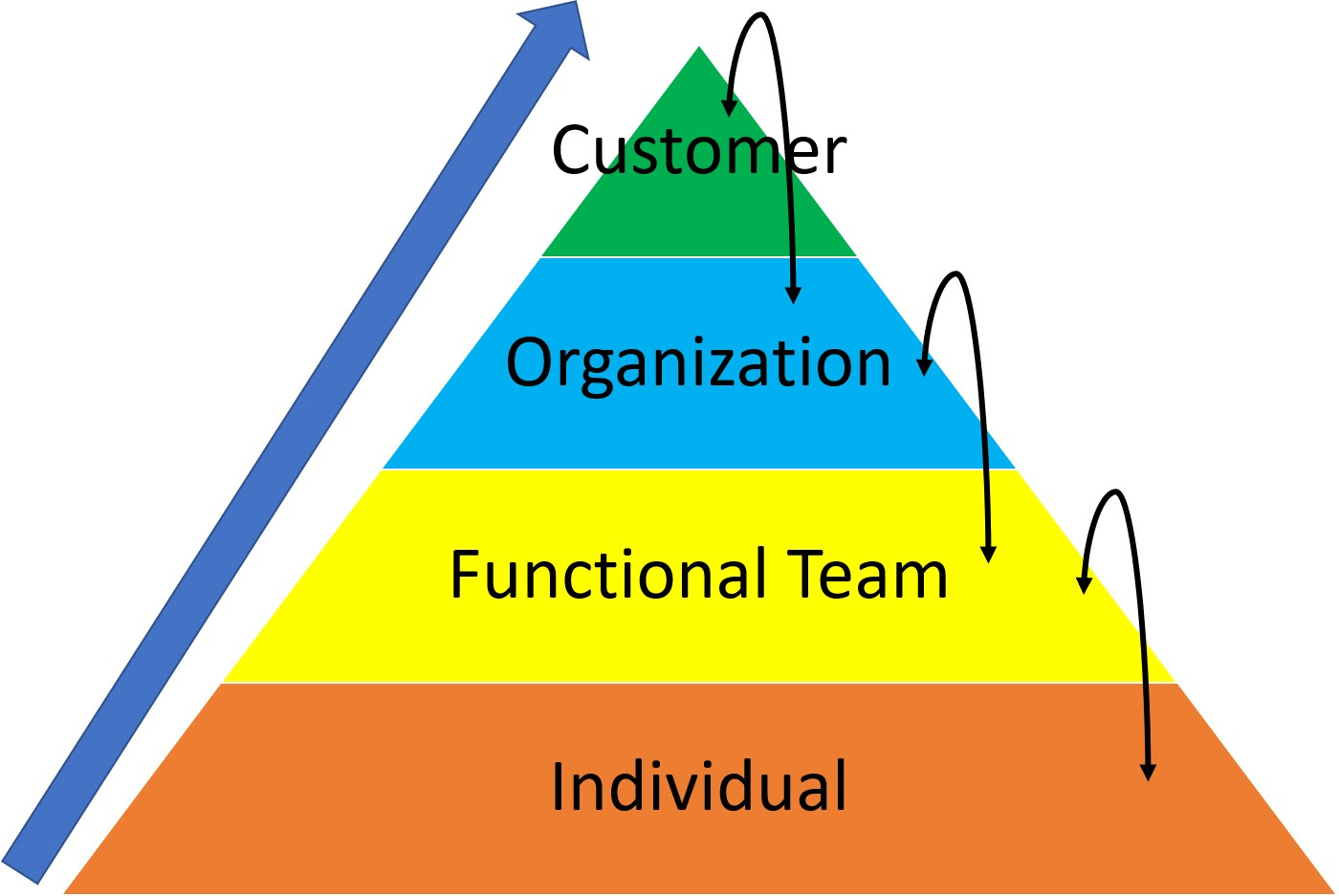
When we make a decision and consider the impact of our decision at a higher level in the hierarchy, as shown in pic, it helps us to make the right decision most of the time.
For example,
as a manager, if you want to do a favor for one of your junior colleagues and the decision will not affect other people in the function or the organization, the decision will be right. If the favor to one person will affect the functional team or even the organization, then the decision may not be the right decision.
i know an entrepreneur with high creditability among his customer's circle, not due to the quality or craftsmanship of his product, but because he always decides in favor of the customer than his organization's short-term expenses. For example, when the customer approaches him for doing the rework in the product due to the customer's mistake of mentioning the wrong specification, he never hesitates to do the rework, and he does it at this expense than arguing with the customer on who is right and what needs to be compensated etc. His generic decision-making thought process puts the higher purpose first than his organization in the short term. In the long run, his decision-making process pays him well as he gets repeated orders from the customers.
My key learning is when we make decisions when we put the higher stakeholder as a priority, likely we will make the right decision, even sometimes, in the short term, we face criticism or pain.
Above all hierarchy of consideration in decision making, listen to your inner consciousness before making any decision, which is more powerful to guide you to make the right decisions than anything else.
Have a great week ahead.
Wednesday, 2 March 2022
Problem Solving Vs. Decision making
Problem Solving Vs. Decision making

In the last few weeks, we have discussed some aspects of emotions that affect the quality of decisions. First, we need awareness about emotions. Second, we need to develop structured problem-solving capability, which to some extent, will help us not to get into the trap of emotional bias in decision making.
What is meant by problem-solving?
Problem-solving is an analytical process to solve the problem. It is more of a structured way of solving the issues.
The problem could be making decisions on the complex business problems like
Should i invest in a new business or not?
Which candidate i recruit, candidate A or Candidate B?
How much inventory do I need to keep to manage the uncertainty?
How should I select the stock as there are plenty of options in the market?
In all the above examples, you have a choice to go ahead with impulsive, emotional decisions or you have an option to apply a structured problem-solving process. Both choices will have an impact on the quality of decisions.
Problem-solving is a process of understanding the facts, removing unnecessary noises in the data, looking for patterns or insights or root causes, making the right actions and implementing the actions, and looking for evidence of improvement.
Problem-solving vs. decision making
Problem-solving is a process, and decision-making is an outcome of problem-solving. Both are interrelated.
If we couple analytical problem solving and decision making, there is a high chance that we are making the right decisions as it is a logical or rational approach than emotional.
Why is problem-solving capability important?
One of the prime responsibilities of a manager or leader is making impactful decisions at the right time. Quality of decision-making will improve only when they learn the art of solving the problem in a structured way, particularly for all chronic or complex business challenges.
The World economic forum lists problem-solving competency as one of the Top 5 competencies for the 21st century. I remembered that the forum survey reported that professionals with problem-solving capability would have more demand and be paid high in the job market.
As i observed, many leaders in organizations who possess excellent problem-solving capabilities will run the organization more effectively than those who lack the same.
Problem-solving and decision-making are competencies each manager and leader to develop for professional growth.
Let us discuss the following insights in the next few weeks.
The process of problem solving and steps involved ;
The myth of the problem-solving approach
The skillset required for problem-solving
Methods of developing the problem-solving competency as an individual and organization
Have a great week ahead.
Awareness of thinking traps in decision making
Awareness of thinking traps in decision making
(Emotional Management for Personal & Professional Growth Series)
As we have discussed the different types of thinking traps that affect our decision-making process, let us summarise the thinking traps and their influence on our decisions.
- Except for routine activities, most of us have decision dilemmas in all business decisions.
- We generally assume that we are logical thinkers and equipped with tools and techniques for decision-making. However, research says that despite all the resources on the rational decision-making process, we are unconsciously trapped into thinking bias which affects the quality of decision making, particularly in complex business decisions.
Some of the thinking traps we have discussed with examples are
- Giving excess weightage to the first information
- Maintaining the status quo even though it is not relevant now
- Seeking confirmation evidence for our initial thought from people who are favoring us
- Not clearly defining the problem itself
- Judgement trap either overconfidence or underestimating.
In every stage of the business decision-making process, we have more stakeholders, more assumptions, and inputs coming from different ends, leading to misperception. This bias influences our choices or decision-making quality.
Some of the above thinking traps can work in isolation, or they can work in combination.
For example, we give more weightage to the first information we receive, believe it true, and seek confirmation from the people in favor of our initial thinking. Then we take some decisions that will become status quo. We stick to it as our sunk cost mentality will not allow us to detach ourselves from our earlier decisions and finally get into the trap of living with the pain of our decision.
The only protection from the different thinking trap is AWARENESS.
Even though we cannot avoid the inputs/assumptions from different stakeholders, we can build tests and be disciplined enough in the decision-making process, which will help to get into the trap. That needs a step back and challenge our thought process while making decisions in important events.
More we take unbiased choices without a trap, our confidence improves.
It is easier said than done; however, it needs awareness and practice to take the unbiased, right decisions in a complex business environment.
Have a great week ahead.
Sunday, 30 January 2022
Judgement Trap in the decision-making process
Judgement Trap in the decision-making process

What is judgement trap?
Most of us are good at predicting the outcome in routine activities like judging the distance, traveling time, some people's responses to particular queries, etc. We do it frequently and adjust our predictions based on experience and feedback.
However, business events are not easy to predict, and poor prediction will affect the quality of decision-making. For example, the commodity price next year and the sales projections for the next three months are all difficult to judge unless we do the judgements too frequently and get feedback to correct our predictions.
In those business decisions, we fall into the trap of overconfidence or underestimate or go by our past experience, which most of the time affects the quality of decision making. That is a judgment trap.
Most organizational growth challenges are not due to people's capability or resource issues. It is primarily due to underestimating the growth potential by the business leaders and not being prepared for it.
In the book "It happened in India," the author Kishore Biyani argued that we had underestimated the growth as a nation, which resulted in a lack of infrastructure. That is a judgement trap, either overestimate or underestimate.
How can we improve our judgement accuracy?
- Expert suggests that instead of anchoring one figure, always go for high and low extreme projections and challenge the assumptions in each scenario, then arrive at some RANGE than sticking on to one fixed no. For example, when estimating the sales projection for next year, look for the ranges in the worst and best scenarios and improve the range instead of fixing one figure.
- We subconsciously go by our memory or experience; it is better to share our judgment with the people who are not biased with the past. They may give better projections that can be considered.
Despite there being many forecasting techniques in the market, we are biased with our thinking of overestimation or underestimation or biased to memory which may affect the decision making.
We need to be aware of the trap when judging future projections or events.
Have a nice week ahead!
Problem defining trap in decision making
Problem defining trap in decision making

As we have been discussing the thinking trap and how it affects our bias in decision-making, one more thinking the trap is "Problem defining trap."
What is meant by a problem-defining trap?
In a daily situation, defining the problem or narrating the situation determines our decision-making quality. When the same problem is defined in two different ways and informed to you, you will react in two different ways, leading to right or wrong decision making.
For example,
You are offered a coupon by online purchase, and it says that you can redeem anytime; you may not react to redeem immediately as you decided to redeem later. In contrast, the offer is said to be redeemed within three days; you decide to redeem it immediately as you inherently do not want to take the risk of losing something.
You are reacting or making decisions based on how the statement is defined.
Similarly, if your customer gives orders to your organization and says that you will get more orders in the future if you deliver on time. You may be doing your best to deliver on time but not too desperate to complete on time. Alternatively, if your customer says that you will be penalized in terms of LD charges if you are not delivering on time, your reaction and decisions would be too aggressive to finish the order on time as you do not want to go through pain.
We are reacting to how the statement or problems are defined and presented to us.
The key learning is how we are defining the statements or defining the problems that eventually determine our decision-making capabilities.
In one of my client organizations, management had poorly reacted to union representatives when they asked for wage revision in absolute terms and ended up with some in-house layoffs and work stoppages. When i reframed the wage increase in terms of proportional value to future sales potential, the management realized that the union's demand was nothing to worry about as the net increase was small compared to sales.
Most of us get into the trap of looking at the problem in fixed ways and get into the thinking trap.
How can we overcome this defining trap?
1. When you are confronting problems, try to practice not to accept as defined by you or others; try to reframe or redefine the situation and look at whether the decision approach is changed or not. That will give you a clue that you are working on a poorly defined problem.
2. When somebody makes a decision, always examine how they framed the problem and challenge their assumption or the definition of the problem. That way, you will learn to look at the problem differently.
Awareness is important as we stick to the problem statement narrated to us, which may lead to the wrong decision-making approach.
Let us discuss another trap next week.
Have a great week ahead!
why do we make wrong decisions? (contd..)
why do we make wrong decisions? (contd..)

What is meant by looking for confirmation evidence for our thought?
We biased our decision-making towards our initial thought even though there are contradictory views or data against our views. We seek people who favor our thinking and even interpret any information according to our thought.
For example,
you would like to purchase an electric vehicle and almost decided to go ahead with an electric type than IC engine. However, you are seeking information from your colleagues. Most of them are against electric vehicles at this moment, citing logical apprehensions like lack of adequate charging facilities, lack of knowledge on maintenance, service support and cost.
Since you have already fixed your mind towards the electric vehicle, you would not listen to any opinion against the electric type or look for a favorable response in line with your initial thought. That is the trap of looking only for confirming evidence for our original thought.
Sometimes we tend to interpret the information according to our initial thought.
There is an old story that goes like this.
In a classroom, a teacher wanted to give a message to the students that consuming alcohol is not good for their health. He demonstrated by taking a glass of alcohol and then putting some insects inside the glass, and eventually, insects died. He said to the students," Look, the alcohol kills the insects; hence it is not suitable for our health.One student stood and said," Sir, I have some insect trouble in my stomach, so by consuming alcohol, i can come out of the trouble, hence consuming alcohol is good for health!".

That is looking for confirmation by interpreting the message as one likes.
The key line, what you want to hear, you will listen to that, and even we distort the information according to our thought. That is the thinking trap.
In the organization setup, we always seek information or go to the people who would like to endorse our views or decision, which may affect the decision-making quality.
How can we overcome this thinking trap?
- We need to ensure whether we give all the options equal weightage or give high weightage for our initial option as ultimate. Awareness of emotions and rationality is key.
- We can weigh our options with many pros and cons than confining with one option; for example, In the electric vehicle purchase case, just i want to buy to be trendy and be open to other pros and cons of purchasing. That openness and flexibility will help to make the right decisions.
Let us discuss other thinking traps next week.
Have a great week ahead!
Why do we make wrong decisions? (contd..)
Why do we make wrong decisions? (contd..)

Justifying the past decision even though it is not relevant now:
We continue to make decisions based on past choices. Even though we believe that we make rational decisions, we sometimes fall into the trap of justifying the past decision even though it is not relevant now or future. Economists term this decision-making behavior as sunk cost fallacy.
For example,
Assume that you have booked a ticket for a movie of your favorite star before releasing. After the film is released, you are getting more negative reviews about the movie, and your logical mind realizes that the movie is a flop.
Will you decide to go with your earlier decision of watching the film as you already booked?
If you decide to drop to watch the movie despite your advance ticket booking cost, you are not falling into the trap of sunk cost fallacy.
If you decide to go and watch since you do not want to waste your invested money, you are in the trap of sunk cost fallacy.
Similarly,
In a stock market, our tendency to average the stock, which is continuously falling. That decision is sunk cost fallacy. We hope that we recover the past investment.
Most of us get into this sunk cost fallacy in decision making, not only from a money perspective, even from the time and efforts we spent on something in the past. That is why in the organization, we use to justify some of our people's mistakes and build decisions over them repeatedly because we have invested our time and effort with them.
Why do we get into this thinking trap?
Internally, we do not want to admit our mistakes or accept the failures and try to cover up the old errors with new efforts or decisions. That is the nature of us.
How to overcome this thinking trap?
1. Even smart, logical decisions sometimes go wrong. Failing is not a sin, but building over the past mistake and making decisions to cover up may lead to blunders which we can avoid with awareness. We need to accept the failures as part of our decision-making process in personal and professional life.
2. Reward yourself and your team for the process of decision-making with available data then, rather than punishing for the outcome. We need to realize that we are making judgments based on some assumptions, and the outcome depends on the various factors. The ability to distinguish between the process and result will help you accept some of the failures in the decisions.
When we make decisions, we are driven by various emotions and need to be aware of those emotions to make better decisions. Awareness is key.
Let us discuss some other thinking traps next week.
Have a great week ahead!
Saturday, 1 January 2022
Why do we make wrong decisions?
Why do we make wrong decisions?

We are discussing the thinking traps which affect our quality of decision making. Last week we discussed the thinking trap of "giving excess weightage to the first information." The second thinking trap is " Not to disturb the status quo."
The term "status quo" can be defined as preserving the existing practices or doing comfortable things.
We believe that we make decisions logically, but our mind prefers to preserve the existing practices or comfort when we make decisions.
For example,
we prefer to go to the office on a fixed route and timings;
being comfortable to deal with a few chosen vendors/customers/banks or people in the business;
having lunch or free time chatting with a few colleagues;
choosing a fixed seating location in a meeting or training session;
sticking with fixed agenda in regular meetings.
We hesitate to disturb what we feel more comfortable to us. That is the nature of our thinking process of not disturbing the status quo.
Why do we have the thinking of sticking on to comfort?
The source for sticking to the status quo or comfort is our internal ego or fear. When there is change, there will be some challenges; we need to take responsibility, there will be some actions that may be favorable or non-favorable, which may affect our status. That is why we prefer to stick to the existing situation as much as possible.
That is the reason when you drive some new initiatives in the organization,it would become a challenge as generally, people do not want to disturb the existing way of familiar working to new way of working.
How to overcome this thinking trap?
- As long as the status quo is not affecting our personal or our business objective, no need to change. Alternatively, if you realize the objective is not achieved due to sticking to the status quo, we need to change it. That awareness or clarity between current status vs. goal is required.
- We need not conclude that the existing status quo is the only option available. We need to be open to multiple options, which can be practiced by asking what else in every decision-making situation.
- Constantly evaluating the cost-benefit analysis in any options against the status quo will help change the perception of sticking to the status quo.
We need to be aware of thinking traps while making decisions.
Let us discuss some other thinking traps next week.
Have a great week ahead!
Why do we make wrong decisions?
Why do we make wrong decisions?

As we have been discussing "making effective decisions," research says that even though we are equipped with many decision-making processes, tools, and techniques, we are psychologically trapped in our thinking process, which affects the quality of decisions we make in our personal life and professional lives.
Let us discuss some of the psychological thinking traps in the coming weeks, as the awareness of the same will help us make better decisions.
One of the most common thinking traps is "Giving excessive weightage to first information" and taking decisions based on it.
For example,
when we meet a person for the first time, we form an internal perception based on the dressings, tone, ascend, or physique. We make decisions based on it. Later on, the reality may be pleasant or unpleasant. That is the thinking trap of giving excessive weightage to the first impression.
similarly,
When we intend to buy a product or property, we may not know its real value. When the seller initiates the price by stating X, we will decide to purchase or negotiate around the value of X only, and the probability of thinking Y is very low since we are anchored too much on the FIRST Information.
When we set the annual sales target in the organization, either the team will go by last year's performance or the past 3 / 5 years average as the mind is anchored to the first-hand information rather than looking beyond.
That is the thinking trap in decision-making.
How to overcome the thinking trap of giving excessive weightage to first information?
- Being aware of our thinking trap when we make important decisions.
- Doing some work beforehand and getting others' opinions so that we may not be confined with only one piece of information. ( some of us do!) for example, as in buying a product at a given X price, do research and get comprehensive data about the product to avoid the anchoring trap.
- Going beyond the past or first information – for example, as in sales target example, rather than working from the past, set the target based on the business's market potential.
It is natural to get into the thinking trap, and being aware of it will help make the right decisions in personal and professional life!
Let us discuss some other thinking traps next week!
Have a great week ahead!
How to overcome decision dilemmas?
In a professional environment, except for routine decisions, many of us get into the decision dilemma. The dilemma is whether we can decide in a given situation, despite sufficient data points and assumptions available. Internally fear of making wrong decisions puts us in a dilemma.
In this process, neither we make decisions nor be peaceful as non-decisiveness puts us in a disturbed state. How do we get the clarity or courage to overcome the dilemma?
For example, consider this situation.
You are head of manufacturing and received a message from your customer that they rejected the recent consignments and would impose the penalty if not replaced quickly. As this situation may typically happen, you can manage on your own. However, you have a dilemma whether you need to inform your boss or not.
Even though the problem is manageable, you have a typical decision dilemma. If you inform your boss, he may get angry with you. If you do not notify your boss, you can avoid the immediate pain of emotional drama. In case if your boss comes to know the issue at a later stage, he would perceive it as an integrity issue, which may be much painful for you. That is a decision dilemma.
Similarly, as a manager or leader, you may have decision dilemmas in many instances like whether to recruit a person for a key role or not, whether to give feedback to a non-performer or not, whether to accept a new assignment or not. You might have come across many situations wherein you stuck to making decisions.
Here, we need to get clarity of our decision vs. consequence by weighing many outcomes.
The simple tool of decision vs. consequence will be helpful to overcome the dilemmas.

As in the above example, if you decide to inform your boss about quality issues, you can list down all the positive and negative consequences. Also, when you decide not to inform your boss, you can list down all the positive and negative consequences. When you list down all the probable positive and negative consequences of "informing" and "not informing," you may get clarity on which path to take.
This simple tool will help to think clearly to overcome the decision dilemma.
We have a mix of emotions that puts us in a dilemma that we can overcome with rational evaluation by correlating decision vs. consequence.
You may try next time when you have a decision dilemma!
Have a great week ahead!
Tuesday, 7 December 2021
i am good at rational decision-making!
i am good at rational decision-making!

As we have discussed some of the myths of decision-making, most of us have one more misconception: "believing that i am good at rational or logical decision-making."
In a professional environment, as a manager or leader, we firmly believe that we make decisions based on the facts, logical conclusions upon data analysis, and structured evaluation of pros and cons. It is not true, and many psychology studies proved that finally, emotions overdrive logic.
Our decisions are driven mainly by emotions which sometimes lead to mistakes or substandard performance.
For example, you might have encountered an experience when you wanted to purchase any gadgets or home appliances. You might have set the budget, decided the mode of purchase, browsed, verified with many people, and decided to buy a particular brand or product. However, at the last moment, that decision might have been changed just by one adverse information or news about the brand /model or even a solid positive opinion about an alternative brand or model by someone close to you. All your logical thinking and decisions were collapsed just by one emotional feeling of "not to be on the wrong side."
I have a personal experience that one of my books was selling reasonably well on Amazon with positive reviews till one anonymous buyer gave an adverse comment about me and the content. Post that review; there was a considerable reduction in the sales performance. The reason could be the reader's buying decision is biased towards "not to be on the wrong side." Logically readers should go by the count of positive vs. negative comments, but reality would be biased to the latest negative comments. That is the power of emotions over any rational or logical thinking.
So, since emotion is so powerful in our decision-making process, we need to be aware of our state of mind when making important decisions in a professional environment like taking calls on people, business expansion, investment, reacting to customer's complaints. Any impulsive decisions we take in an extreme emotional state will lead to a wrong or negative consequence.
The next option is to defer the decision when we are highly emotional.
Awareness is required on emotional state when we make a decision!
Have a great week ahead!
How does decision-making improve self-confidence?
How does decision-making improve self-confidence?

As we are discussing the myths about decision making, one of the myths is that self-confident people are capable of making decisions as they are sure in their thinking process to select the right choices. It may be partially true as naturally, the decision-making is obvious for them.
In reality, not all people are confident in all circumstances. One finding says that 85 % of people suffer from low self-esteem, affecting communication and decision-making capability in the professional environment. How to improve the confidence of those people to make better decisions?
In my personal experience, whenever i struggle with low confidence in any aspect, i use to make decisions and then act on them in a small way; eventually, it improves my confidence.
The process goes like this. When we decide to work on any issues, there is always a 50 % probability of success. That probability of success will give positive reinforcement to take slightly higher-level decisions and actions. Inturn that likelihood of success leads to making even more higher-level decisions and actions. In that way, an individual can increase confidence.
For example,
Most of us have fear in public speaking or stage fear to communicate the idea or present. When you decide to crack and plunge into action by addressing a few of your known colleagues or friends, you positively reinforce speaking in a small gathering.
Next time, when you decide to do it in a larger audience of known people, your subconscious mind pushes positively, as you already demonstrated in a small group. So, you can make it relatively easy.
Next time, when you decide to do it in a larger audience of unknown people, your previous decision and success positively push you to do it well.
By doing so many times, your confidence in public speaking improves as you primarily decide to do it.
Hence, when you make a small series of decisions and actions in any professional challenges or workplace issues, the probability of success makes you a more confident person rather than being a confident person makes you a good decision-maker.
As a professional, the more you motivate yourself to take a series of minor decisions and actions, eventually, that will make you more confident in your professional life.
Have a great week ahead.
